Description
Overview:
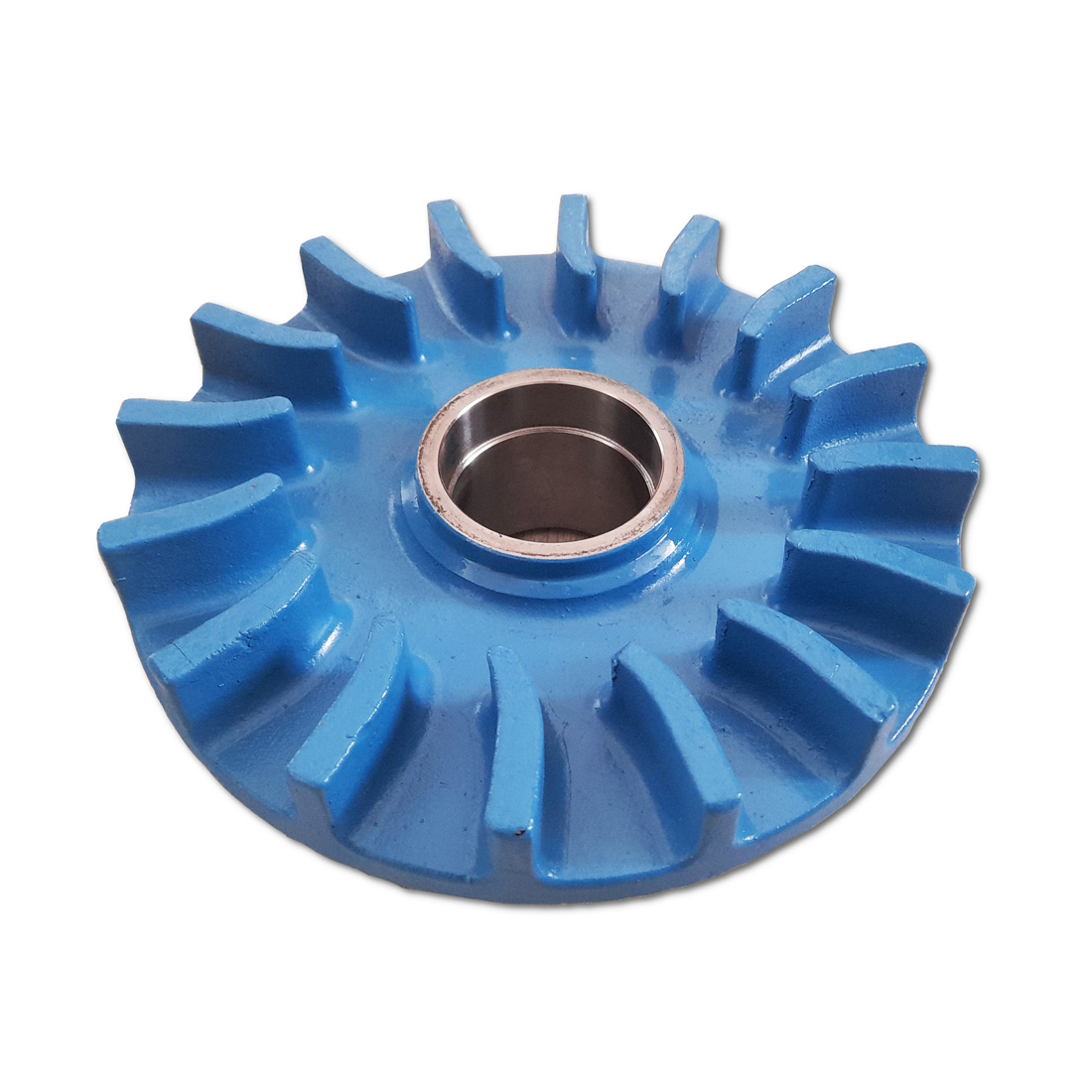
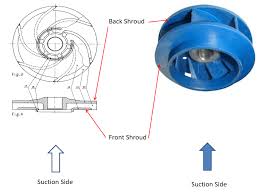
The impeller is the dynamic heart of a centrifugal pump, transferring energy from the motor to the fluid. Its design features vanes extending from an open central inlet, generating centrifugal force that propels liquid to the discharge point. Various impeller types offer distinct performance characteristics, making them suitable for specific applications.
Key differences among impeller types include:
– Flow characteristics: Optimized for specific flow rates and patterns
– Efficiency: Design and size impact overall efficiency
– Pressure handling: Suited for different pressure ranges
– Material compatibility: Constructed from materials compatible with specific fluids and applications
– Maintenance and repair: Designed for ease of maintenance and repair
Understanding Impeller Types:
There are five primary types of impellers, each with unique characteristics, advantages, and applications:
1. Open Impeller: Exposed vanes without protective shrouds, suitable for smaller pumps with low strain and some solid content.
2. Semi-Open Impeller: Back-wall shroud provides mechanical strength, suitable for medium-sized pumps with small amounts of soft solids.
3. Closed Impeller: Enclosed vanes provide maximum strength and efficiency, ideal for large pumps transferring clean liquids.
4. Vortex Impeller: Designed for handling dirty fluids with debris and stringy solids, creating a whirlpool effect to prevent damage.
5. Cutter Impeller: Designed to handle solids by grinding and obliterating them, ideal for pumping sewage and waste.
Impeller Diameter:
The impeller diameter significantly impacts pump performance. A larger diameter results in higher circumferential speed, increased head, and flow. Impellers can be trimmed to meet specific duty points, but excessive trimming can lead to efficiency losses.
Selecting the correct impeller type and size is crucial for optimal pump performance, efficiency, and longevity. By understanding the unique characteristics and advantages of each impeller type, you can make informed decisions to ensure your centrifugal pump meets your specific application needs.























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.